
The core inflation rate in the United States remained steady at 2.9% in August, according to the latest data. This figure aligns with economists’ forecasts and provides a clearer picture of the current economic landscape. The stability in core inflation, which excludes volatile food and energy prices, is a key indicator monitored by the Federal Reserve as it considers future monetary policy decisions.
This latest report offers a mixed bag of signals for the Fed. While the steady core inflation rate might suggest that previous interest rate hikes are having the desired effect of cooling down price pressures, other economic indicators, such as rising jobless claims, add complexity to the decision-making process. The Fed is carefully weighing these factors as it contemplates potential interest rate adjustments in the coming months.
Inflation Data: A Closer Look
Key Components of the Inflation Rate
Understanding the components of the inflation rate is crucial for assessing the overall economic health. The core Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) price index, which is the Fed’s preferred inflation gauge, focuses on the underlying trend of inflation by excluding volatile items. This provides a more stable measure for policymakers to base their decisions on.
The August report indicated that while overall inflation saw some increases, the core rate remained consistent. This suggests that the price increases were primarily driven by factors outside of the core components, such as energy or food prices, which are subject to more frequent fluctuations. These factors are often influenced by global events and supply chain dynamics.
Impact on Consumer Spending
Inflation directly impacts consumer spending habits. When prices rise, consumers typically have less purchasing power, which can lead to reduced spending on non-essential goods and services. This can then have a ripple effect on businesses, potentially leading to decreased revenues and slower economic growth.
The fact that core inflation has remained steady may provide some reassurance to consumers, as it suggests that the underlying price pressures are not escalating rapidly. However, consumers are still closely watching prices and adjusting their spending accordingly. Monitoring consumer sentiment and behavior is essential for understanding the broader economic implications of inflation.
Expert Analysis and Forecasts
Economists and market analysts are closely scrutinizing the inflation data to forecast future trends and potential impacts on the economy. The consensus among experts is that while inflation has shown signs of cooling, it remains above the Federal Reserve’s target of 2%. This means that the Fed is likely to maintain a cautious approach to monetary policy.
Many analysts believe that the Fed will continue to monitor economic data closely before making any further adjustments to interest rates. The timing and magnitude of any future rate cuts will depend on a variety of factors, including inflation, employment, and overall economic growth. Keeping an eye on expert analyses and forecasts can help individuals and businesses make informed financial decisions.
The Federal Reserve’s Response
Monetary Policy Tools
The Federal Reserve has a range of monetary policy tools at its disposal to manage inflation and promote economic stability. One of the primary tools is adjusting the federal funds rate, which influences interest rates throughout the economy. By raising interest rates, the Fed can make borrowing more expensive, which can help to cool down inflation. Conversely, lowering interest rates can stimulate economic growth by making borrowing cheaper.
In addition to adjusting interest rates, the Fed can also use tools such as quantitative easing (QE) and forward guidance to influence economic conditions. QE involves the Fed purchasing assets, such as government bonds, to inject liquidity into the financial system. Forward guidance involves communicating the Fed’s intentions and expectations to the public, which can help to shape market expectations and behavior.
Balancing Inflation and Economic Growth
The Federal Reserve faces the challenge of balancing the need to control inflation with the desire to promote economic growth and maintain stable employment. Raising interest rates too aggressively could risk slowing down the economy and potentially triggering a recession. On the other hand, failing to address inflation could lead to rising prices and erode consumer purchasing power.
The Fed’s decisions are therefore carefully calibrated to strike a balance between these competing objectives. The central bank closely monitors a wide range of economic indicators and considers the potential impacts of its policies on different sectors of the economy. The goal is to achieve sustainable economic growth while keeping inflation under control.
Potential for Future Rate Cuts
The steady core inflation rate in August has raised questions about the potential for future interest rate cuts by the Federal Reserve. While some analysts believe that the Fed may begin to consider rate cuts in the coming months, others argue that it is too early to predict with certainty. The Fed is likely to remain data-dependent and will carefully assess economic conditions before making any decisions.
The timing and magnitude of any future rate cuts will depend on a variety of factors, including the trajectory of inflation, the strength of the labor market, and overall economic growth. The Fed has emphasized that it is committed to achieving its dual mandate of price stability and full employment. Any decisions regarding interest rates will be guided by these objectives.
Market Reactions and Economic Outlook
Stock Market Response
The stock market’s reaction to the inflation data has been relatively muted. Investors are closely watching economic indicators for clues about the future direction of monetary policy. The stability in core inflation has provided some reassurance, but concerns remain about the overall economic outlook.
Market participants are also focused on other factors, such as corporate earnings, geopolitical events, and trade policies. These factors can all influence market sentiment and contribute to volatility. Investors are advised to remain cautious and diversified in their investment strategies.
Impact on Bond Yields
Bond yields are also influenced by inflation expectations and monetary policy. When inflation is expected to rise, bond yields typically increase to compensate investors for the erosion of purchasing power. Conversely, when inflation is expected to fall, bond yields tend to decrease.
The steady core inflation rate in August has contributed to some stability in bond yields. However, yields remain sensitive to economic data and Fed policy announcements. Investors in fixed income securities should closely monitor these factors.
Overall Economic Outlook
The overall economic outlook remains uncertain, with a mix of positive and negative indicators. While the labor market has remained relatively strong, there are signs that economic growth is slowing. Inflation has shown signs of cooling, but it remains above the Federal Reserve’s target.
Economists and policymakers are closely monitoring these developments to assess the potential risks and opportunities facing the economy. The future trajectory of the economy will depend on a variety of factors, including government policies, global economic conditions, and technological innovation. Staying informed about economic trends and developments is essential for making sound financial decisions.
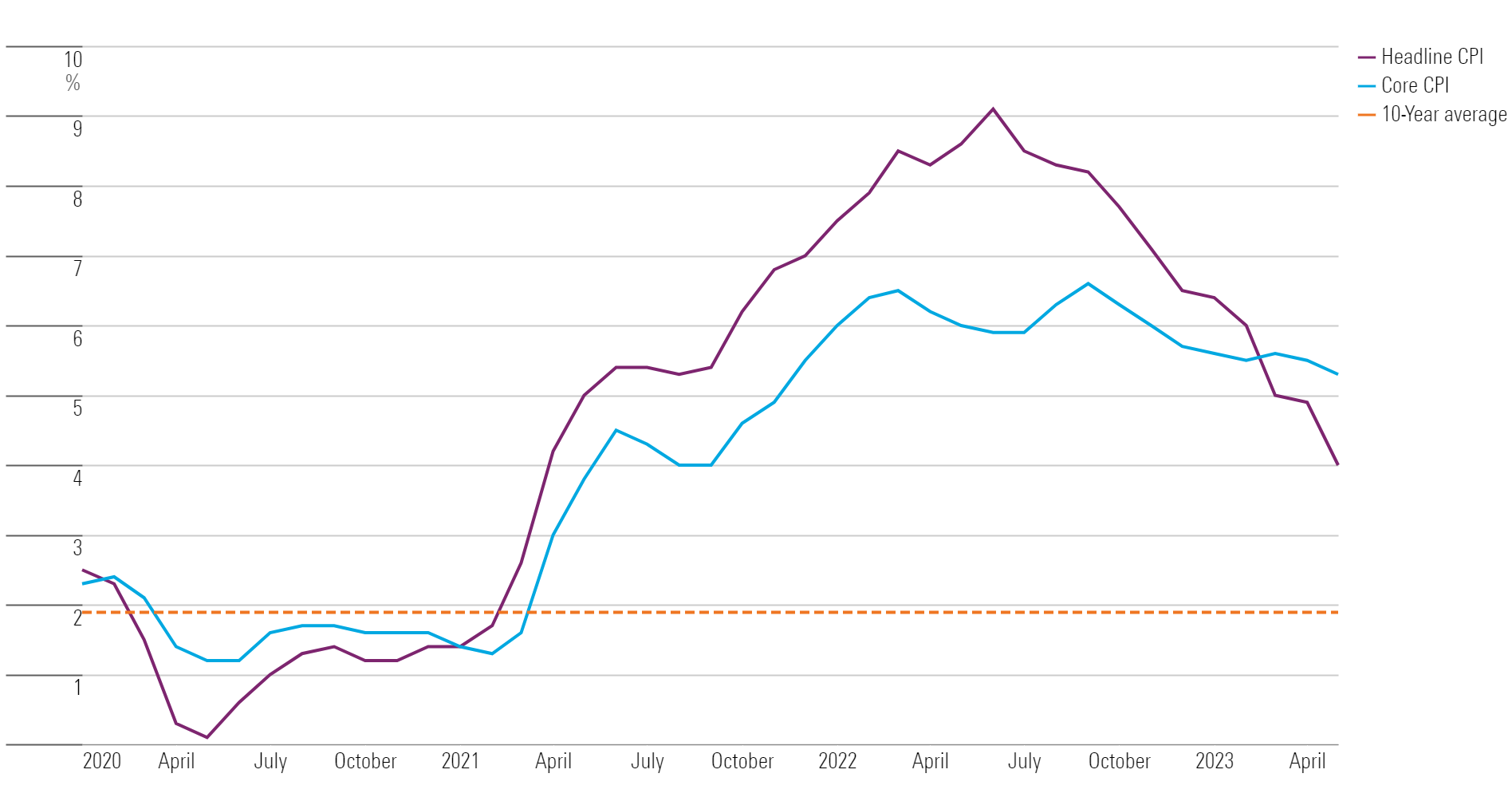
A graphical representation of the core inflation rate remaining steady at 2.9% in August, reflecting the Fed’s gauge.
Key Takeaways
- Core inflation held steady at 2.9% in August, meeting expectations.
- The Federal Reserve is carefully monitoring inflation data as it considers future interest rate adjustments.
- The stability in core inflation may provide some reassurance to consumers and investors.
- The overall economic outlook remains uncertain, with a mix of positive and negative indicators.
- Market reactions have been relatively muted, with investors closely watching economic data and Fed policy announcements.
FAQ
What is core inflation?
Core inflation is a measure of inflation that excludes volatile components such as food and energy prices. It provides a more stable view of underlying price pressures in the economy.
Why does the Federal Reserve focus on core inflation?
The Federal Reserve focuses on core inflation because it is a better indicator of the long-term trend of inflation. Volatile components can distort the overall inflation rate and make it difficult to assess the true underlying price pressures.
How does inflation affect consumers?
Inflation affects consumers by reducing their purchasing power. When prices rise, consumers can buy less with the same amount of money. This can lead to reduced spending and slower economic growth.
What are the Federal Reserve’s tools for managing inflation?
The Federal Reserve has several tools for managing inflation, including adjusting the federal funds rate, quantitative easing, and forward guidance. These tools can influence interest rates, liquidity in the financial system, and market expectations.
What is the current economic outlook?
The current economic outlook is uncertain, with a mix of positive and negative indicators. While the labor market has remained relatively strong, there are signs that economic growth is slowing. Inflation has shown signs of cooling, but it remains above the Federal Reserve’s target. For further insights, consider related coverage.
How might steady inflation impact future Fed decisions?
The steady inflation rate might give the Federal Reserve room to consider future policy adjustments, potentially including rate cuts, depending on other economic factors. However, the Fed will likely proceed cautiously, analyzing various data points before making any significant changes.
What role does consumer spending play in the overall inflation rate?
Consumer spending is a significant driver of inflation. Increased demand can lead to higher prices, while decreased demand can lead to lower prices. Monitoring consumer spending patterns is crucial for understanding inflationary pressures.
How do global events influence domestic inflation rates?
Global events, such as supply chain disruptions or geopolitical tensions, can significantly impact domestic inflation rates. These events can affect the prices of imported goods and raw materials, which can then pass through to consumers.
Conclusion
The core inflation rate holding steady at 2.9% in August provides a snapshot of the U.S. economy at a critical juncture. While this stability may offer some reassurance, the Federal Reserve remains vigilant, carefully assessing a range of economic indicators to guide future monetary policy decisions. As consumers and investors navigate this landscape, staying informed and adaptable is key to making sound financial choices. Continue to monitor economic reports and analyses to stay ahead of potential shifts in the economic climate.

