
Recent reports indicate a concerning rise in polio cases in both Pakistan and Nigeria, threatening global eradication efforts. These new cases highlight the persistent challenges in combating the highly infectious disease, particularly in regions with low vaccination rates and complex socio-political landscapes.
The resurgence of polio demands immediate and coordinated action to prevent further spread and protect vulnerable populations. Health officials and international organizations are intensifying vaccination campaigns and strengthening surveillance systems to address the outbreaks effectively.
Polio’s Return: A Closer Look at Pakistan and Nigeria
Pakistan’s Escalating Polio Count
Pakistan has reported a significant increase in polio cases in 2024 and 2025. As of September 2025, the nation’s polio tally has risen to 26, with new cases emerging in areas like Khyber Pakhtunkhwa (KP) and Tank. This surge is particularly alarming given the country’s ongoing efforts to eradicate the virus.
The affected regions often face challenges such as vaccine hesitancy, logistical difficulties in reaching remote areas, and security concerns that hinder vaccination campaigns. These factors contribute to the virus’s continued circulation and the emergence of new cases.
One recent case involved a child in Tank, raising the district’s total and contributing to the overall national increase. Health authorities are working to identify and vaccinate contacts of those infected to prevent further transmission. For more details, you can read related coverage.
Nigeria’s Fight Against Resurgence
Nigeria, once declared polio-free, has also reported new cases, signaling a potential resurgence of the virus. While the exact number of recent cases remains less publicized than in Pakistan, the situation underscores the fragility of polio eradication and the need for sustained immunization efforts.
The challenges in Nigeria include reaching children in conflict zones, addressing misinformation about vaccines, and ensuring consistent funding for immunization programs. The country’s vast and diverse population also presents logistical hurdles in delivering vaccines to every child.
Rotary International’s President-elect has warned that Nigeria risks a polio resurgence if routine immunization is not maintained and strengthened. This highlights the critical role of ongoing vaccination campaigns in preventing outbreaks and protecting vulnerable communities.
Factors Contributing to Polio Resurgence
Vaccine Hesitancy and Misinformation
Vaccine hesitancy remains a significant obstacle in both Pakistan and Nigeria. Misinformation and conspiracy theories about vaccines can lead to lower vaccination rates, leaving communities vulnerable to polio outbreaks. Addressing these concerns requires targeted communication strategies and community engagement to build trust and promote the benefits of vaccination.
In some areas, cultural or religious beliefs may also contribute to vaccine hesitancy. Health workers need to be sensitive to these factors and work with community leaders to address concerns and encourage vaccination. Building strong relationships with local communities is essential for overcoming resistance and ensuring high vaccination coverage.
Effective communication campaigns should focus on providing accurate information about the safety and efficacy of polio vaccines. These campaigns should also address common misconceptions and concerns, using clear and accessible language. Engaging trusted community members, such as religious leaders and elders, can help to amplify these messages and build confidence in vaccination programs.
Logistical and Security Challenges
Reaching every child with polio vaccines can be a daunting task, particularly in remote or conflict-affected areas. Logistical challenges, such as poor infrastructure and limited access to healthcare facilities, can hinder vaccination efforts. Security concerns, including attacks on health workers, can also disrupt vaccination campaigns and put frontline workers at risk.
In Pakistan, security threats in certain regions have made it difficult for health workers to access communities and administer vaccines. These threats not only endanger the lives of health workers but also undermine efforts to eradicate polio. Stronger security measures and community support are needed to protect health workers and ensure the safe delivery of vaccines.
Innovative strategies, such as mobile vaccination teams and community-based outreach programs, can help to overcome logistical challenges and reach children in hard-to-reach areas. Collaboration with local communities and organizations is also essential for ensuring the success of vaccination campaigns. By working together, health authorities and community members can overcome obstacles and protect vulnerable populations from polio.
Inadequate Surveillance Systems
Effective surveillance systems are crucial for detecting and responding to polio outbreaks. Weak surveillance systems can delay the identification of new cases, allowing the virus to spread undetected. Strengthening surveillance systems requires investment in training, equipment, and data management.
In both Pakistan and Nigeria, efforts are underway to improve surveillance systems and enhance the capacity to detect and respond to polio outbreaks. This includes training health workers to recognize the symptoms of polio and report suspected cases promptly. It also involves strengthening laboratory capacity to confirm cases and track the spread of the virus.
Real-time data analysis and mapping can help to identify high-risk areas and target vaccination efforts more effectively. By using data to inform decision-making, health authorities can optimize resources and maximize the impact of vaccination campaigns. Strong surveillance systems are essential for monitoring progress towards polio eradication and preventing future outbreaks.
Global Implications and Eradication Efforts
The Impact on Global Polio Eradication
The resurgence of polio in Pakistan and Nigeria poses a significant threat to global eradication efforts. These countries are among the last remaining polio-endemic nations, and continued transmission of the virus could undermine progress made elsewhere. The global polio eradication initiative, led by organizations such as the World Health Organization (WHO) and UNICEF, aims to eliminate polio worldwide.
The recent setbacks in Pakistan and Nigeria highlight the need for renewed commitment and increased investment in polio eradication. This includes strengthening vaccination campaigns, improving surveillance systems, and addressing the underlying factors that contribute to polio transmission. International collaboration and coordination are essential for achieving the goal of a polio-free world.
The WHO and UNICEF are working closely with national governments and local communities to implement comprehensive polio eradication strategies. These strategies include routine immunization, supplementary immunization activities (SIAs), and surveillance for acute flaccid paralysis (AFP). By working together, these organizations are striving to overcome the challenges and achieve the ultimate goal of eradicating polio from the planet.
International Response and Support
The international community has mobilized to support polio eradication efforts in Pakistan and Nigeria. Donor countries and organizations are providing financial and technical assistance to strengthen vaccination campaigns and improve surveillance systems. This support is crucial for sustaining progress and preventing further outbreaks.
The Global Polio Eradication Initiative (GPEI) is a key player in coordinating international efforts to eradicate polio. The GPEI brings together partners such as the WHO, UNICEF, Rotary International, and the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) to implement comprehensive polio eradication strategies.
In addition to financial and technical assistance, international organizations are also providing expertise and guidance to national governments and local communities. This includes training health workers, developing communication strategies, and implementing innovative approaches to reach children in hard-to-reach areas. By working together, the international community is helping to ensure that every child has the opportunity to be vaccinated against polio.
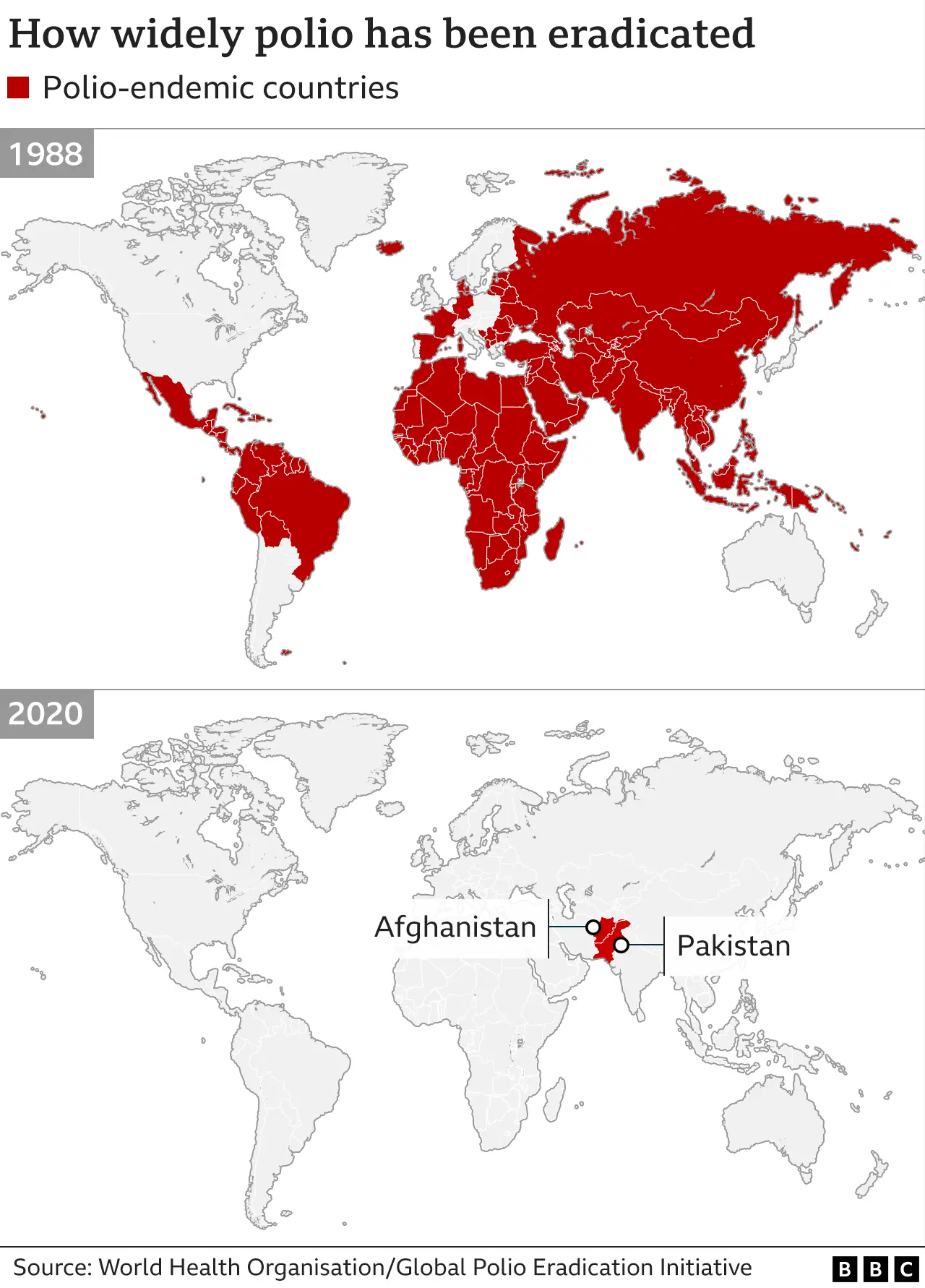
A map illustrating the remaining polio-endemic regions, underscoring the challenges in Pakistan and Nigeria report new polio cases and achieving global eradication.
Strategies for Strengthening Eradication Efforts
Enhancing Vaccination Campaigns
Effective vaccination campaigns are the cornerstone of polio eradication efforts. These campaigns must be well-planned, well-resourced, and effectively implemented to reach every child with the polio vaccine. This requires careful coordination between health authorities, community leaders, and international organizations.
Strategies for enhancing vaccination campaigns include improving vaccine supply chains, training health workers, and developing targeted communication strategies to address vaccine hesitancy. It also involves using innovative approaches, such as mobile vaccination teams and community-based outreach programs, to reach children in hard-to-reach areas.
Monitoring and evaluation are essential for ensuring the effectiveness of vaccination campaigns. This includes tracking vaccination coverage rates, identifying gaps in coverage, and implementing corrective measures to address these gaps. By continuously monitoring and evaluating vaccination campaigns, health authorities can ensure that they are reaching the target population and achieving the desired impact.
Improving Surveillance and Response
Strong surveillance systems are crucial for detecting and responding to polio outbreaks. These systems must be able to identify new cases quickly and accurately, allowing health authorities to take prompt action to prevent further spread of the virus. This requires investment in training, equipment, and data management.
Strategies for improving surveillance and response include training health workers to recognize the symptoms of polio and report suspected cases promptly. It also involves strengthening laboratory capacity to confirm cases and track the spread of the virus. Real-time data analysis and mapping can help to identify high-risk areas and target vaccination efforts more effectively.
Rapid response teams should be established to investigate and respond to new polio cases. These teams should be equipped with the resources and expertise needed to conduct thorough investigations, identify contacts of those infected, and implement appropriate control measures. By responding quickly and effectively to new cases, health authorities can prevent further transmission of the virus and protect vulnerable populations.
Addressing Underlying Factors
Polio transmission is often linked to underlying factors such as poverty, poor sanitation, and lack of access to healthcare. Addressing these factors is essential for creating a sustainable environment for polio eradication. This requires a multi-sectoral approach involving collaboration between health, education, water and sanitation, and other relevant sectors.
Strategies for addressing underlying factors include improving access to clean water and sanitation, promoting hygiene education, and strengthening healthcare systems. It also involves empowering communities to take ownership of their health and participate in polio eradication efforts. By addressing the root causes of polio transmission, health authorities can create a healthier and more resilient environment for all.
Community engagement is essential for addressing underlying factors and promoting sustainable change. This includes working with community leaders, religious leaders, and other influential members of society to build trust and promote positive health behaviors. By engaging communities in the polio eradication process, health authorities can ensure that efforts are culturally appropriate and sustainable in the long term.
Key Takeaways
- Pakistan’s polio cases have risen to 26 in 2025, concentrated in areas like Khyber Pakhtunkhwa.
- Nigeria faces a potential polio resurgence, requiring sustained immunization efforts.
- Vaccine hesitancy, logistical challenges, and weak surveillance systems contribute to the problem.
- International support and enhanced strategies are crucial for global eradication efforts.
FAQ
What is polio?
Polio, or poliomyelitis, is a highly infectious viral disease that primarily affects young children. The virus is transmitted through contaminated water or food and can cause paralysis, which is often irreversible. In severe cases, polio can be fatal.
How is polio prevented?
Polio is prevented through vaccination. The polio vaccine is safe and effective and can protect children for life. Vaccination campaigns are essential for reaching every child with the vaccine and preventing outbreaks of the disease.
Why are polio cases increasing in Pakistan and Nigeria?
Several factors contribute to the increase in polio cases in Pakistan and Nigeria, including vaccine hesitancy, logistical challenges in reaching remote areas, and security concerns that hinder vaccination campaigns. Weak surveillance systems can also delay the identification of new cases, allowing the virus to spread undetected.
What is being done to address the polio outbreaks?
Health authorities and international organizations are working to address the polio outbreaks in Pakistan and Nigeria through enhanced vaccination campaigns, improved surveillance systems, and targeted communication strategies to address vaccine hesitancy. International support and coordination are essential for sustaining progress and preventing further outbreaks.
What can individuals do to help?
Individuals can help by ensuring that their children are vaccinated against polio and by supporting vaccination campaigns in their communities. They can also help to spread accurate information about vaccines and address misconceptions and concerns. By working together, individuals and communities can help to eradicate polio and protect future generations from this devastating disease.
The fight against polio is far from over. The recent increase in cases in Pakistan and Nigeria serves as a stark reminder of the challenges that remain. Continued vigilance, sustained commitment, and innovative strategies are essential for achieving the goal of a polio-free world. By working together, we can overcome these challenges and protect vulnerable populations from this devastating disease.

